Producing Synthetic Fuels from Renewable Feeds
Scott Sayles, Robert Ohmes, Pattabhi Raman Narayanan and Jessica Hofmann
A comprehensive review of renewable processes and feedstocks used in the production of renewable or synthetic fuels. Below is an expert from the article recently published in Decarbonisation Technology – February 2024 issue. https://ptqmagazines.digitalrefining.com/view/528948587/52/
The method of synthetic fuel production is dependent on the ability to meet the requirements of a circular economy. The feed used to produce the synthetic fuels determines how it fits into the circular economy and within the carbon lifecycle. For example, the use of a renewable feed, such as woody waste, produces a renewable fuel that is consumed and has a carbon value that is about net zero.
Many of the processes used to produce renewable fuels are identical or very similar to those used for fossil fuels. The critical difference is that both the feedstock and the energy used in the conversion processes must be certified as renewable. The main processes to convert renewable feedstocks into these renewable or synthetic fuel products are discussed.
Renewable feedstocks
- Plant oils and animal fats
- Sustainable biomass
Renewable processes
- Anaerobic digestion
- Gasification
- Pyrolysis
- Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL)
- Pretreatment
- Hydroprocessing
- Fluid catalytic cracking (FCC)
- Hydrogen production
- Ammonia synthesis
- Methanol production
Renewable and synthetic fuels
- Biogas
- Renewable diesel
- Biodiesel
- Renewable jet and sustainable aviation fuel (SAF)
- Hydrogen
- Ammonia
- Methanol
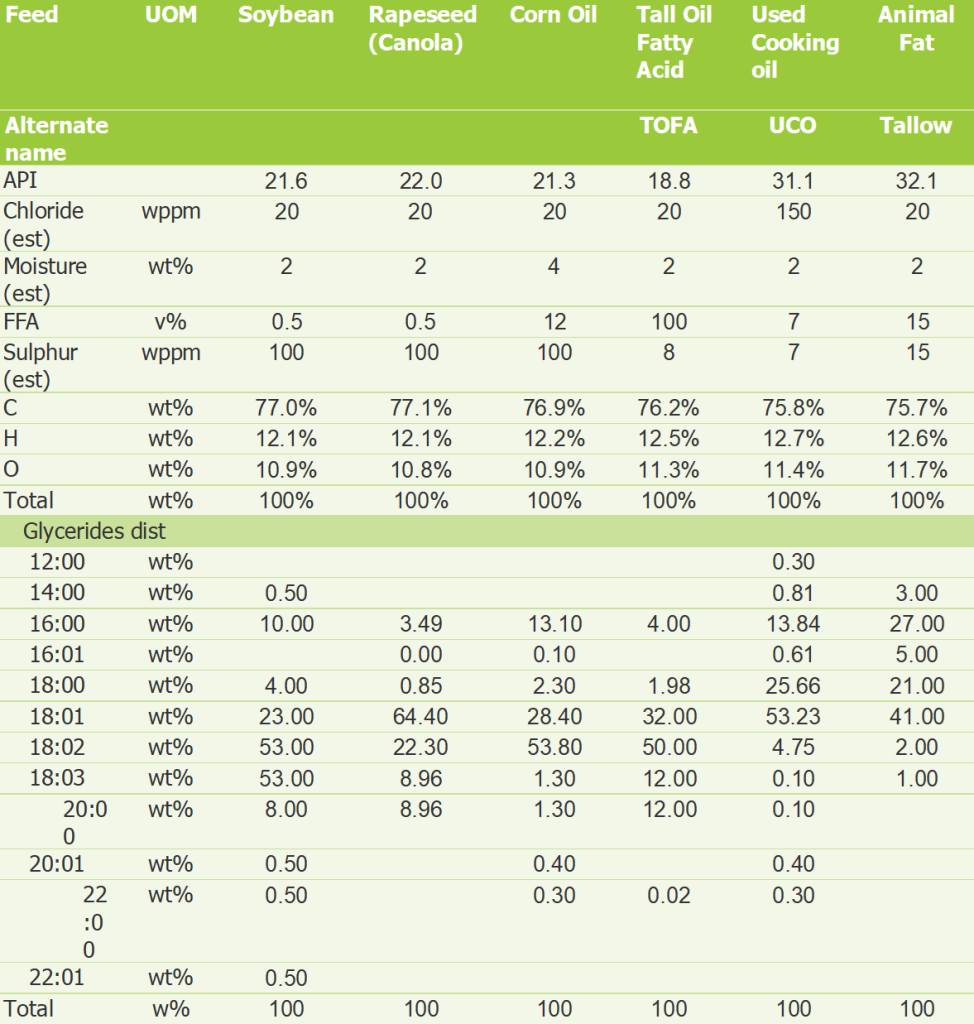
Typical Renewable Feeds: Seed Oils and Animal Fats